计算机基础结构
生词
| 英文 | 中文 |
|---|---|
| Terminology | 术语 |
| general-purpose | 多功能 |
| assembly language | 汇编语言 |
| instruction set | 指令集 |
| architecture | 架构 |
| Von Neumann | 冯诺依曼 |
| Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU) | 算术逻辑单元 |
| Program Counter (PC) | 程序计数器 |
| volatile | 不稳定的 |
| firmware | 固件 |
| scenario | 情景 |
| mnemonic | 帮助记忆的 |
| executable | 可执行的 |
| synchronization | 同步 |
| communication bus | 通讯总线 |
一些 Intel x86 指令
| 含义 | 指令 |
|---|---|
| move | MOV |
| push | PUSH |
| push all | PUSHA |
| move with sign | MOVSX |
| load address | LEA |
| add | ADD |
| subtract | SUB |
| multiplicate | MUL |
| divide with sign | IDIV |
| logical and | AND |
| bit test | BTS |
| bit scan forward | BSF |
冯诺依曼架构
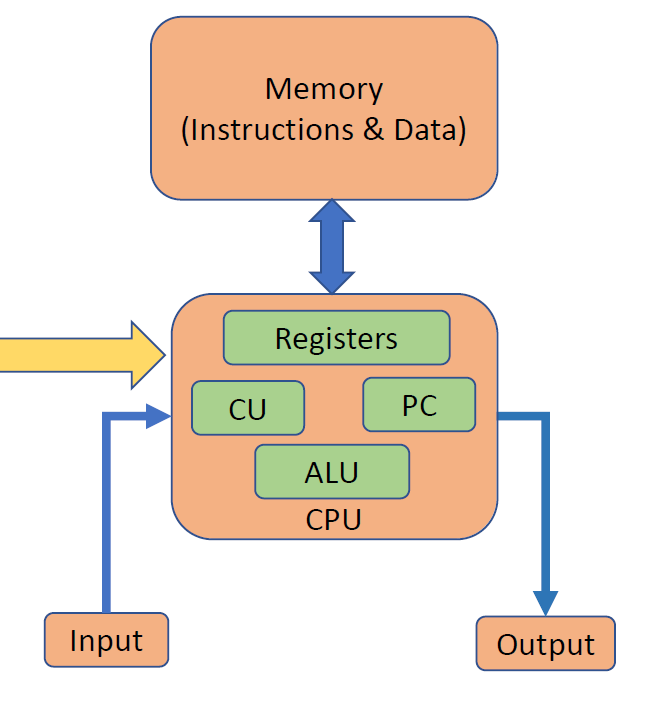
其中:
- CU 是 Control Unit,用于从主存储器获取指令(fetch)到 CPU
- PC 是 Program Counter,用于保存指令的地址
- ALU 是 Arithmetic & Logic Unit
很多现代计算机都使用冯诺依曼架构
ASCII
使用 7 个 bits 来表示 128 个字符
word
1 word = n bytes = 8n bits
GB 和 GiB
- GB: 1000 MB
- GiB: 1024 Mib
内存寻址
How much memory can be addressed when using 1-byte memory address?
Answer: 256 Bytes
(pdf page 22)
意思是,8 位寻址空间,可用内存 256 字节
类似地,如果是 32 位,那就是 4GiB
汇编语言简介
| 指令名称 | 简称 |
|---|---|
| addition | add |
| subtraction | sub |
| load word | lw |
| store word | sw |
| shift right logical | srl |
| branch if not equal | bne |
注意 PC
根据 CPU 架构,程序计数器(PC)可能指向当前正在执行的指令、正在获取的指令或下一条可执行指令。
机器周期
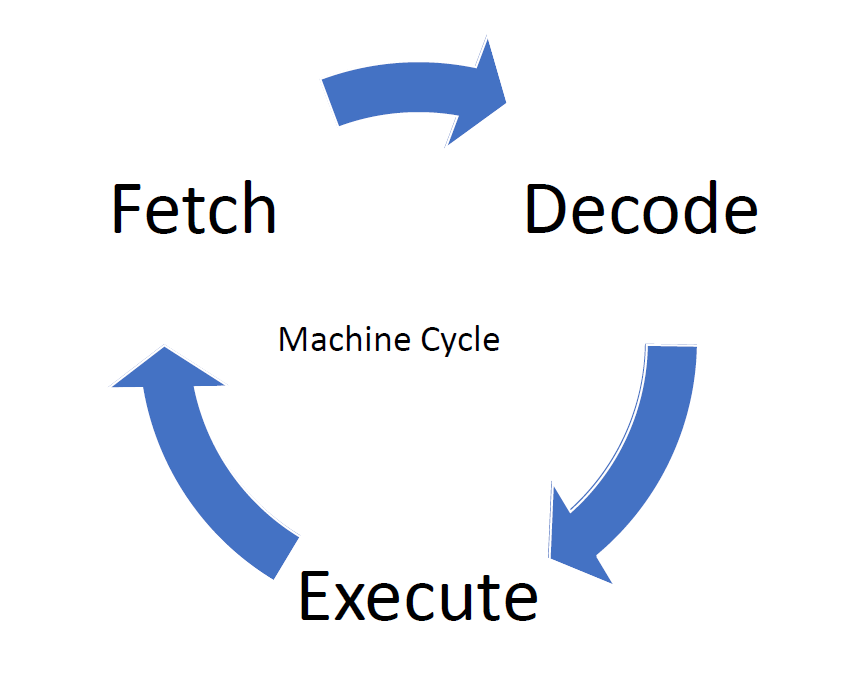
其中,fetch 和 execute 过程受 CPU 当中 CU 的控制,fetch 到的指令会被安排到 instruction register 当中。每当一条指令被执行,program counter 就会增加,以便存储下一条指令。